You can create a SQL Server database using either SQL Server Management Studio or command line T-SQL.
In SQL Server, there are two types of databases:
- System Databases: Automatically created when SQL Server is installed. For example: Master, MSDB, Model, Tempdb, Resource.
- User Databases: Contains user specific data and is created by users after SQL Server installation.
Please note that a database name must be unique within a SQL Server instance and can contain up to 128 characters.
Creating database using SSMS
Under Object Explorer, right click on database and select “New Database” option.

Enter database name. You can optionally review values under “Options” and “Filegroups” page to add more customization to your new database.
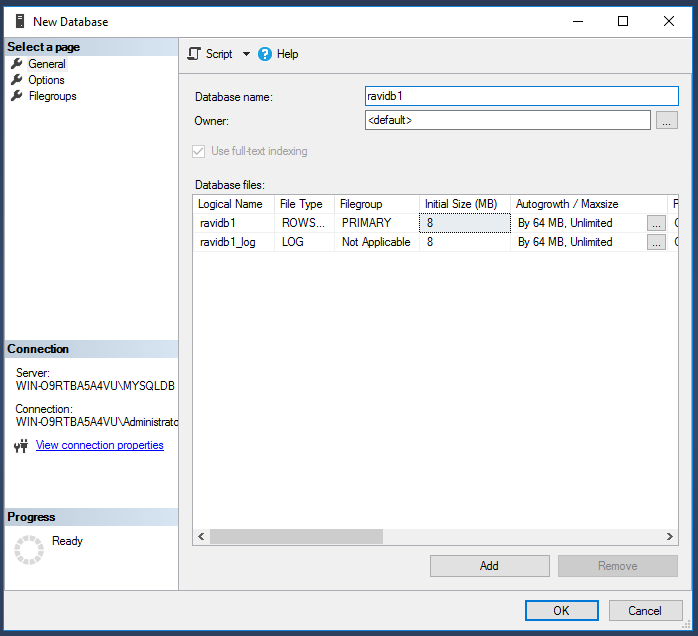

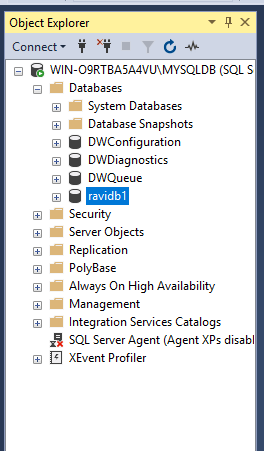
Click OK to create the database. The new database can be seen under object explorer.
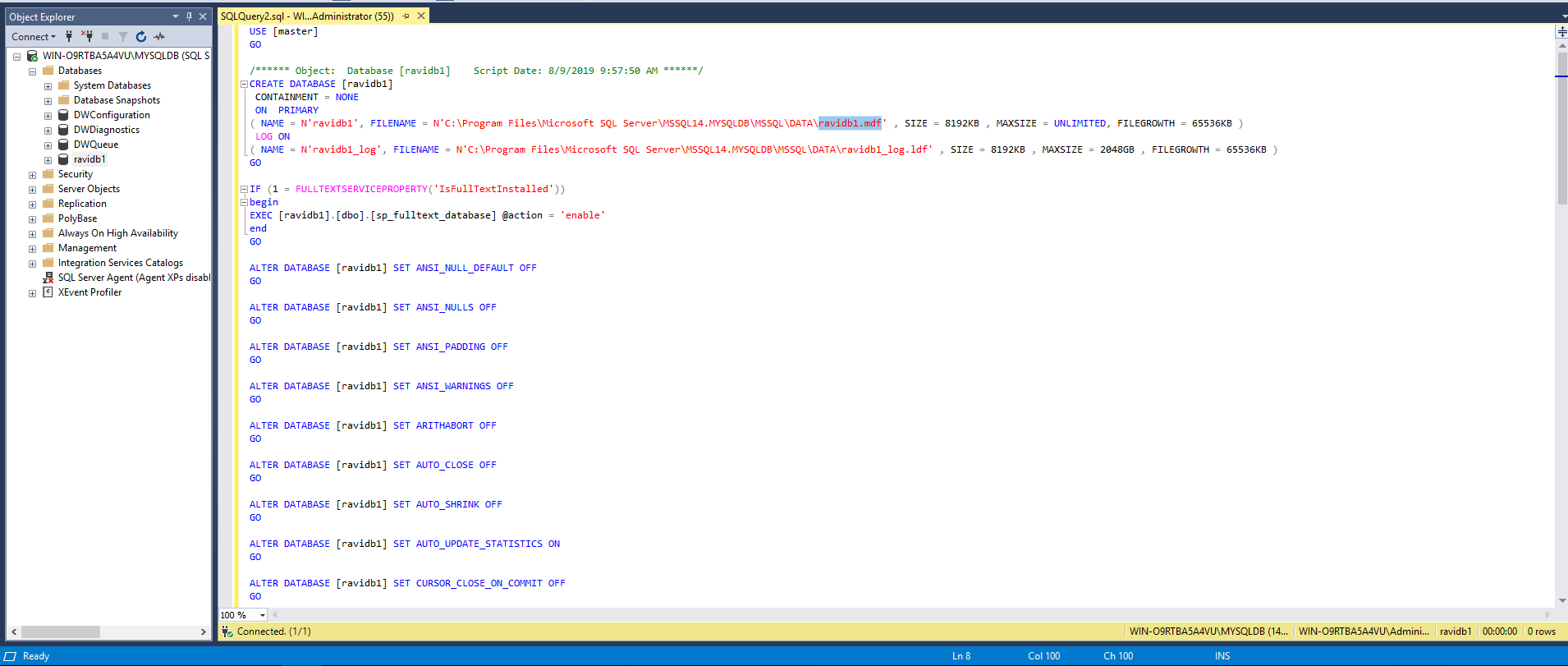
You can review/export the database creation script as follows:

Click on “New Query Editor Window” to view the database creation script.
Creating Database using T-SQL
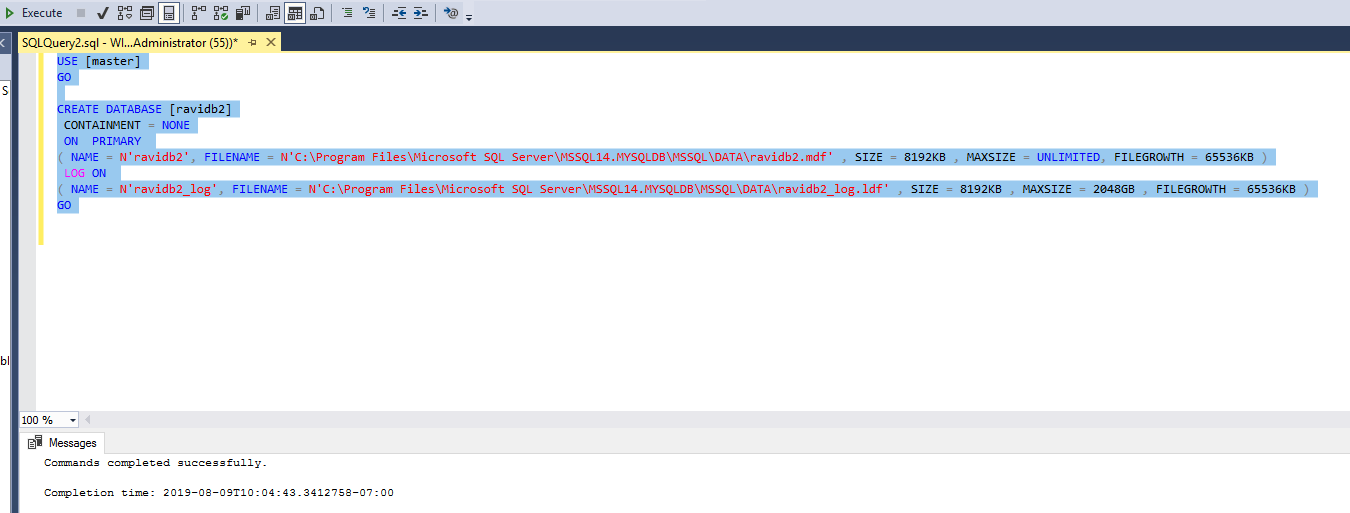
You can use the script from above and modify it to create your database using T-SQL. This is especially helpful if you want to automate the process on several machines. Here’s the simple T-SQL i used to create a new database ravidb2.
USE [master]
GOCREATE DATABASE [ravidb2]
CONTAINMENT = NONE
ON PRIMARY
( NAME = N’ravidb2′, FILENAME = N’C:\Program Files\Microsoft SQL Server\MSSQL14.MYSQLDB\MSSQL\DATA\ravidb2.mdf’ , SIZE = 8192KB , MAXSIZE = UNLIMITED, FILEGROWTH = 65536KB )
LOG ON
( NAME = N’ravidb2_log’, FILENAME = N’C:\Program Files\Microsoft SQL Server\MSSQL14.MYSQLDB\MSSQL\DATA\ravidb2_log.ldf’ , SIZE = 8192KB , MAXSIZE = 2048GB , FILEGROWTH = 65536KB )
GO
I had to disconnect and reconnect object explorer to see the new database “ravidb2” there.
Please Note: For creating or altering database, statement must be run in auto-commit mode. SSMS is in auto-commit mode by default.
